- Specialization
- Individuals and countries can be made better off if they will produce in what they have a comparative advantage and then trade with others for whatever else they require
- Absolute and Comparative Advantage
- Absolute Advantage
- The producer that can produce the most output or requires the least amount of inputs
- Comparative Advantage
- The producer with the lowest opportunity cost
- Input vs. Output
- Output shows the data as products produced given a set of resources.
- Outcome, result.
- Input shows the data as amount of resources needed to produce a fixed amount of output
- Time.
Friday, May 18, 2018
absolute vs comparative, input vs output
balance payment
- Balance of payments
- A measure of money inflows as well as outflows in the U.S. and the world.
- Three Accounts
- Current Account:
- Net Exports
- Exports give credit
- Imports give debit
- Net Foreign Income
- Income that is earned by foreign assets.
- Net Transfers
- Foreign aid
- Capital Account:
- This is the balance of capital ownership.
- Investments in the U.S.
- Purchase of financial assets by the foreigners.
- Official Reserves:
- Foreign currency holdings given by the Federal Reserve System.
- Balance of Goods and Services
- Goods exports +|- services exports - (goods imports + service imports)
- Balance on Current account
- Balance of good= services + net investment + net transfers.
- Official Reserves
- Current account + Capital Account = 0
Phillip's curve
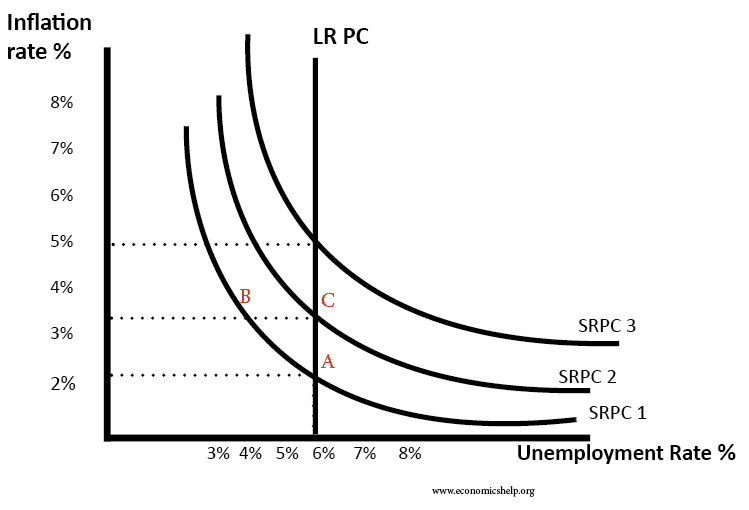
- Phillips Curve
- There is an inverse relationship between inflation and unemployment. Each point on the Phillip's Curve corresponds to a different level of output.
- Long Run
- Occurs at the natural rate of unemployment.
- It is represented by a vertical line.
- LRPC
- Long Run Phillips Curve will only shift if the LRAS shifts.
- Unemployment
- NRU is equal to frictional, seasonal, and structural unemployment.
- Short Run
- Since wages are sticky, inflation changes move the point on the SRPC.
- If inflation persists, then the entire SRPC moves up.
- Stagflation
- Unemployment and inflation simultaneously rise.
- Supply Shocks
- Rapid and significant increases in resource cost.
- If inflation expectations drop due to new technology or efficiency, then the SRPC will move downward.
- Misery Index
- Combination of inflation and unemployment in any given year.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
absolute vs comparative, input vs output
Specialization Individuals and countries can be made better off if they will produce in what they have a comparative advantage and then t...
-
Phillips Curve There is an inverse relationship between inflation and unemployment. Each point on the Phillip's Curve correspon...
-
E lasticity of demand-A measure of how consumers will react to a change in price I nelastic demand [needs] - the demand for a goo...